How Reliable is the Pencil Test for Expediting the Patent Prosecution Process?
By Nathan Phares, Associate
Many patent practitioners and Examiners have spoken of the “pencil test,” which suggests that an independent claim is more likely to be rejected or is rejected as a matter of course if the claim is shorter than a pencil laid upon the claim. Some point to the pencil test as a useful rule of thumb and suggest “padding” the length of the independent claim in hopes of improving the outcomes of prosecution. However, drafting a lengthy independent claim may unnecessarily narrow the scope of the claim. Does the length of the independent claim truly impact prosecution outcomes, or is the pencil test a myth? We’ve analyzed the data, and we provide our conclusions below.
The data set we created for this analysis includes all patents that issued from applications filed post-AIA. We limited the scope of the data set to electrical, mechanical, chemical, and biotech tech centers (i.e., Tech Centers 1600, 1700, 2100, 2400, 2600, 2800, 3600, and 3700). For each patent, the data set indicates the number of Office Actions (OAs), the Art Unit and Tech Center, the length of claim 1 in total words and unique words, the length of the specification, and various other data (e.g., number of RCEs, Assignee, Agent, pendency, and so on). We didn’t filter for unusually long or short claims – the longest claims (topping out at over 8,000 words!) and the shortest claims seem to generally be legitimate.
According to the data, first-OA allowances are slightly more likely with a longer independent claim than with a shorter independent claim, suggesting that the pencil test may be a factor in first-OA allowances. Figure 1 shows a chart of the average number of total words in Claim 1 for buckets of the number of OAs. First-OA allowances, which are associated with zero OAs, have a slightly longer first claim on average than second-OA allowances. This relationship holds across all the Tech Centers we analyzed except TC 1600. Figure 2 shows a chart of the average number of unique words in Claim 1. In Figure 2, the same impact is present but is far less pronounced, indicating that total word count is more strongly correlated with first-OA allowance than unique word count.
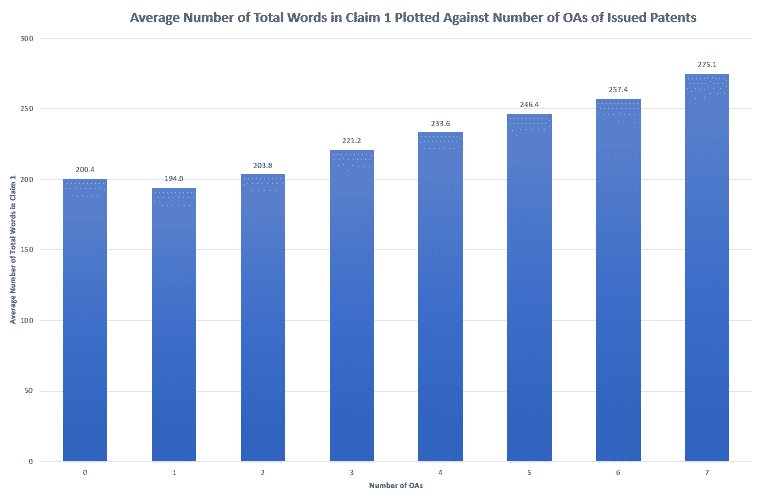
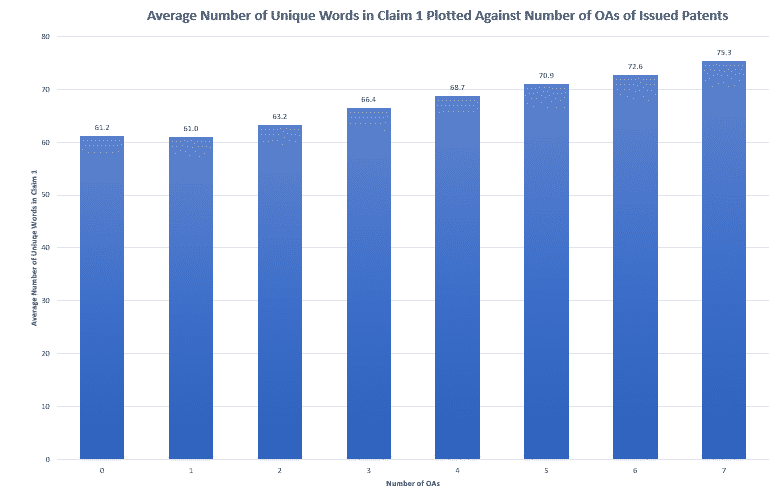
The pencil test seems not to predict outcomes other than first-OA allowances: as the number of OAs before allowance increases, so does the length of claim 1. This is the opposite of what the pencil test would suggest and may reflect the tendency to amend features into claim 1 over the course of prosecution in pursuit of allowance.
As the data shows, independent claims that include more total words tend to receive better treatment at the outset of prosecution, but outcomes are not clearly impacted by the pencil test as prosecution continues. Therefore, the patent drafter should consider lengthening the independent claim if a first-OA allowance is the goal. However, the data shows that the impact of the pencil test is mild at best, so the drafter should not rely on claim length alone to carry the day. For example, the art unit where the application is assigned is a powerful predictor of the efficiency of the patent prosecution. Therefore, the drafter should consider how the language used in the application may impact the assignment of the art unit.
It is important to note the limitations of the data set. First, the claim lengths shown above are claim lengths of the issued patent, not of the patent application when it is first examined. Thus, it is hard to tell whether the correlation between claim length and length of prosecution is due to the amendment of features into claim 1. Second, we omitted patents associated with 8 or more OAs from the charts above, since the data set gets quite sparse after 7 OAs – for example, the 10, 11, 12, and 13 OA buckets collectively represent only 59 patents. However, the trend shown in Figures 1 and 2 continues through the 9 OA bucket.

