Getting To Know Your Patent Examiner Through Data
Law360 (June 13, 2019) — How many office actions should I expect at the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office? Should I file a request for continued examination or a notice of appeal? Is it worth filing a pre-appeal?
These, among others, are common questions that practitioners may ask themselves during patent prosecution. In the past, these were mostly questions that could not be answered by taking into account unique proclivities of different examiners. Now, using data analytics, we can get a better sense of how prosecution will go and be able to make an informed decision when a crossroad is reached.
Below, we will explore how to use public data about an examiner, provided by the USPTO, during patent prosecution.
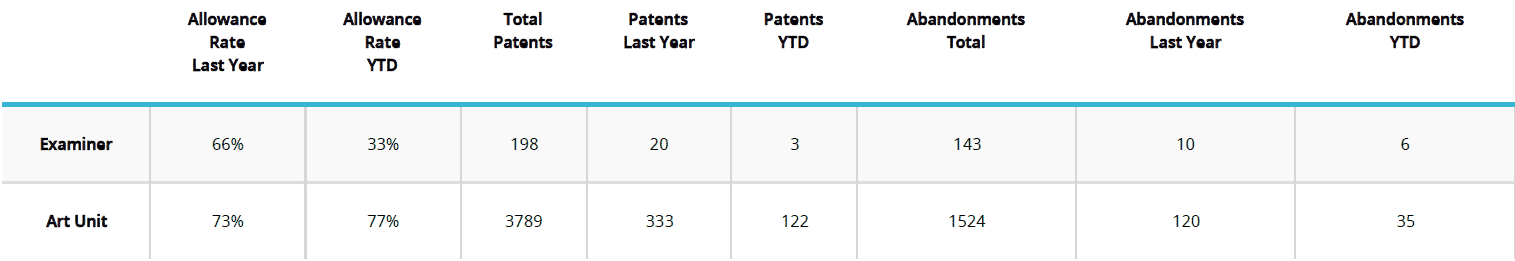
Allowance Rate
.jpg)
By looking at an examiner’s allowance rate (i.e., allowance vs. abandonments), we can get a sense of the journey early on. A high allowance rate is an indicator that the examiner likely has no qualms about allowing applications, and that the examiner likely will not stubbornly stick to poor rejections. For these types of examiners, if appropriate, it may be worth taking a more assertive initial position, including arguing that the rejections should be withdrawn, or offering modest amendments.
However, if the examiner’s allowance rate is low, you may want to consider including substantial amendments or anticipate the possible need to file an appeal as these types of examiners tend to combine three, four, or even five-plus references in their art rejections. If the allowance rate in the art unit is significantly higher than the examiner’s allowance rate, you may want to consider getting the examiner’s supervisor or a primary examiner in the art unit involved early in the process as it may be easier to reach an agreement with them than with the assigned examiner.
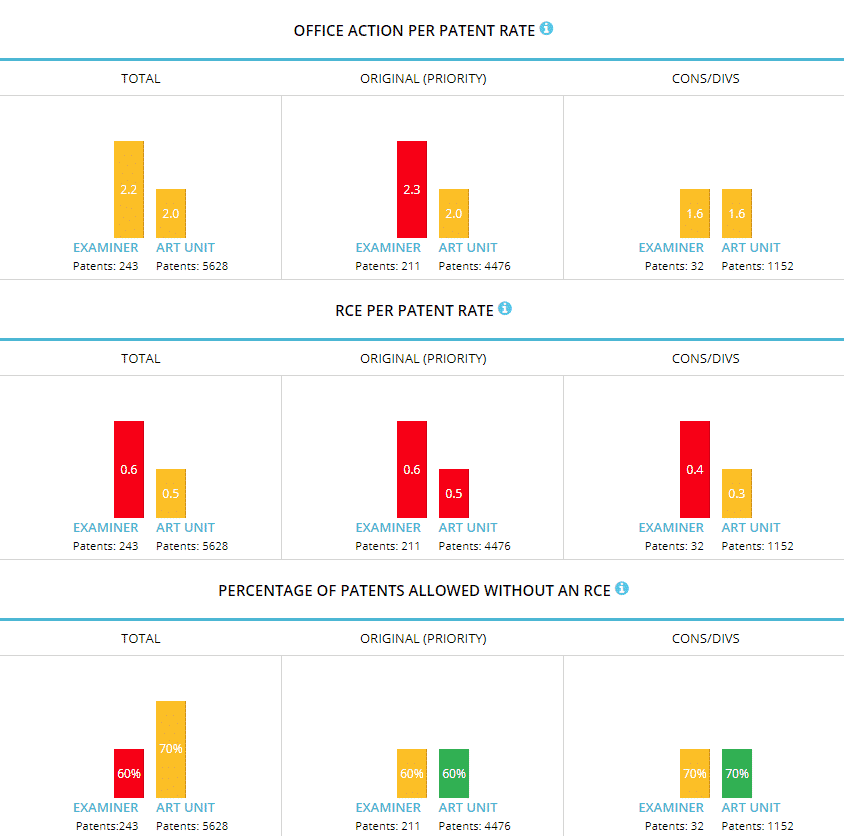
Office Actions Per Patent, RCEs Per Patent

A high office action per patent and/or RCE per patent rate may be an indication that reaching allowability will be challenging. These types of examiners also are likely unafraid to combine three, four or five-plus references to make their art rejections. Similar to examiners with low allowance rates, you may want to consider including substantial amendments, getting the supervisory examiner or a primary examiner involved, or planning to file an appeal. You may even want to check the supervisory examiner’s and primary examiner’s allowance rates when deciding whether to get one of them involved.
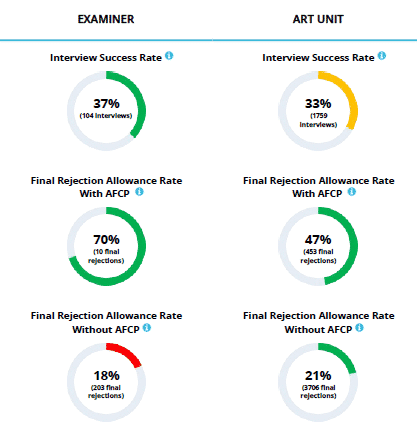
Interview Statistics

Generally speaking, it is beneficial to interview an examiner as it gives a practitioner an opportunity to get a better sense of the examiner’s interpretations of the application and the applied references, and a chance to explain the invention.
A high interview success rate (i.e. the rate that interviews lead to an allowance in the next office action) may be an indicator that the examiner uses interviews for compact prosecution. These examiners are likely willing to provide suggestions for amendments that would lead to allowance or at least advance prosecution. For these types of examiners, you may want to be prepared to discuss multiple, different types of amendments to take advantage of their willingness to expedite prosecution. However, if the interview success rate is low for the examiner, consider sending a substantive interview agenda with proposed amendments to maximize the chance of reaching an agreement with the examiner.
A comparison of an examiner’s final rejection allowance rate with After Final Consideration Pilot and his/her final rejection allowance rate without AFCP may be an indicator of whether the examiner takes the AFCP program seriously. If there is a significant difference with those rates, the examiner likely uses the allocated two to three hours in the AFCP program to find a way to allow the application. For these types of examiners, consider filing an after-final amendment with an AFCP request before deciding whether to file an RCE or a notice of appeal. However, if the rates are similar, the examiner likely uses pre-pilot procedures regardless of whether an AFCP is filed.
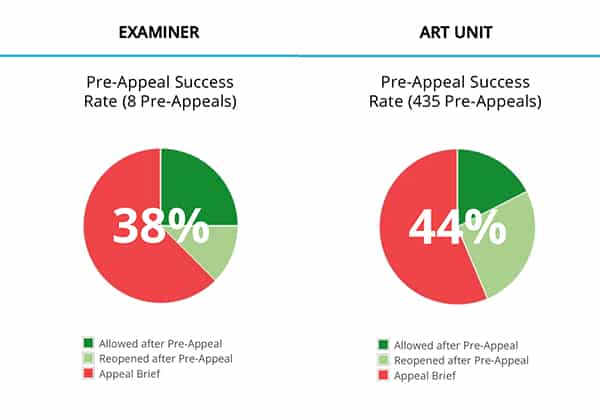
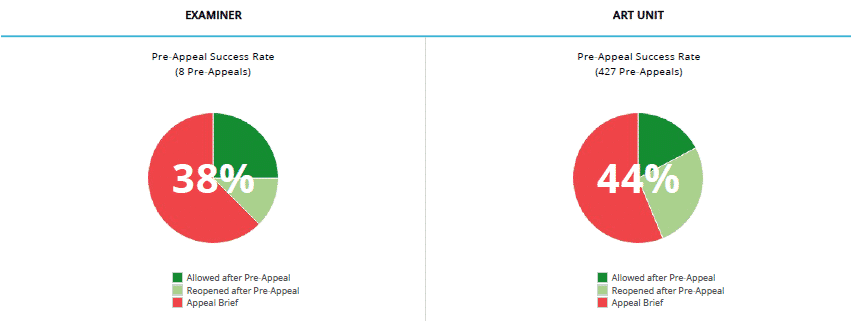
Pre-Appeal Statistics

Pre-appeal statistics can be useful when deciding whether to file an appeal brief or a pre-appeal brief. A high rate of allowance and/or re-opening of prosecution when pre-appeals are filed may indicate that the examiner, the examiner’s SPE, and other panel members in the examiner’s art unit take the pre-appeals process seriously and that it is worth presenting arguments in a pre-appeal brief. However, a low rate of allowance and a low rate of reopening of prosecution after pre-appeal may indicate that it would be better to forego the pre-appeal process and go straight to appeal or go another round with an RCE.
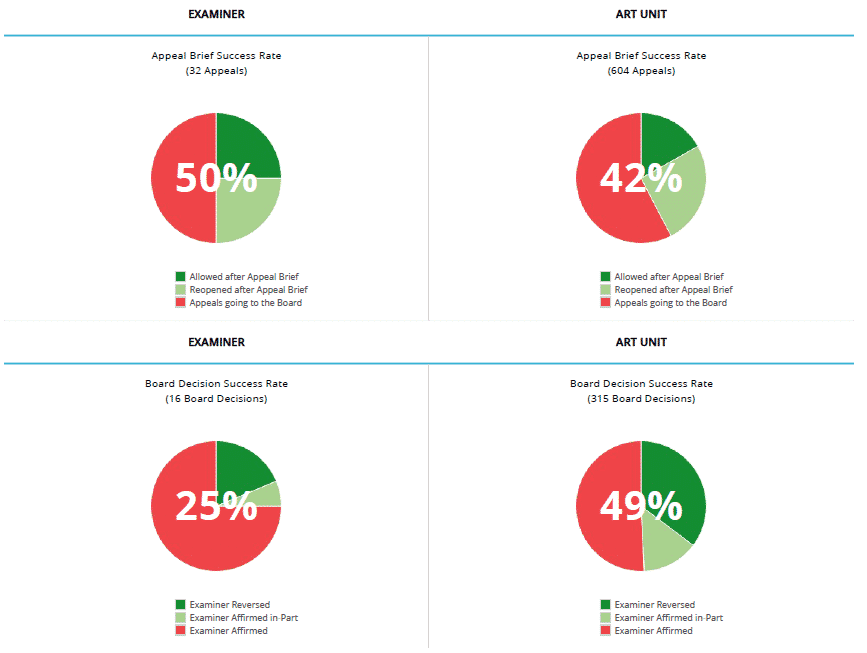
Appeal Statistics

Analyzing an examiner’s appeal statistics may be useful in determining whether to file an appeal or an RCE. If the examiner’s rate of allowance after an appeal is filed is high, it may be worth appealing rather than filing an RCE and avoid narrowing claims unnecessarily. However, if the examiner’s rate of allowance after appeal is low, it is highly likely that your appeal will go to the Patent Trial and Appeal Board.
Since it may take a couple of years for the PTAB to pick up your appeal due to their backlog, you may want to make certain that your client is comfortable with going through with the appeals process and waiting rather than filing an RCE and possibly reaching an agreement with the examiner earlier. For these types of examiners, you may want to consider the examiner’s allowance rate and RCEs per patent rate to help you and your client in making this decision.
If the examiner’s board decision success rate is high, it may be an indication that the examiner goes to the board only when he/she believes that his/her examiner’s answer would be particularly strong. If you receive a compelling examiner’s answer from these types of examiners, consider filing an RCE rather than going to the board.
Conclusion
Just like how data analytics has improved efficiency in other industries, examiner analytics has the potential to improve the efficiency of patent practitioners and patent prosecution. Therefore, using examiner data in your practice may lead to better, quicker and cheaper outcomes for you clients.
By Kris Rhu
The example screenshots in this article are from Patentprufer, which was developed by Harrity & Harrity.