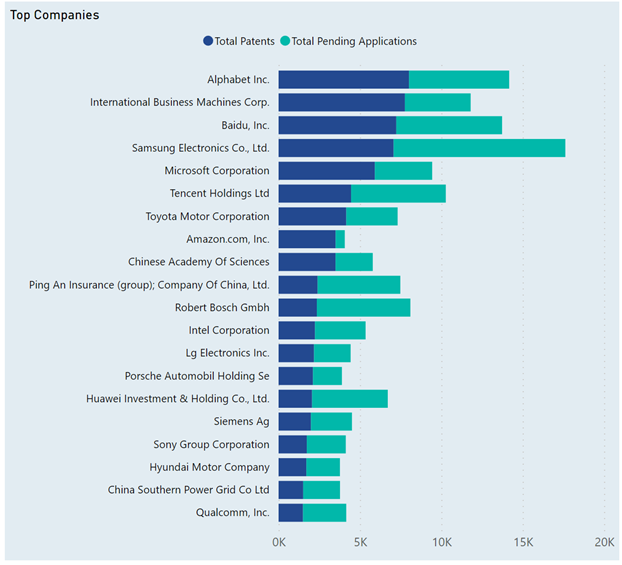
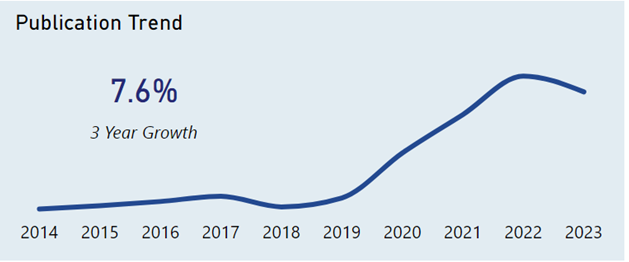
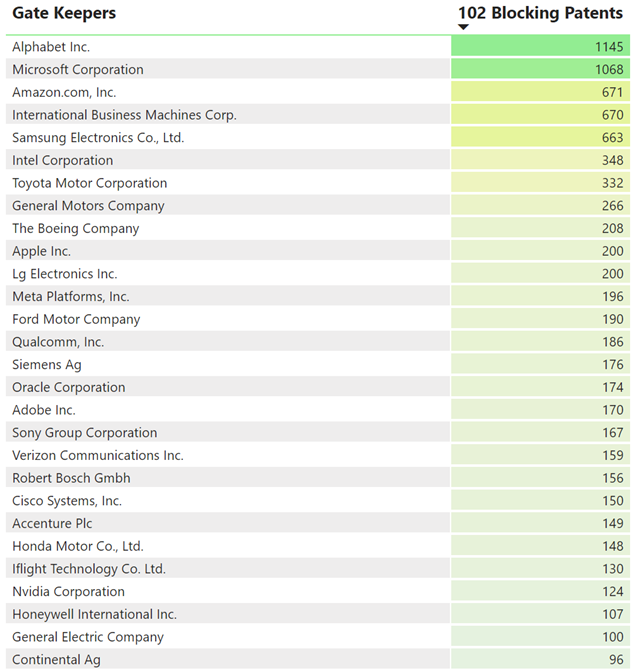
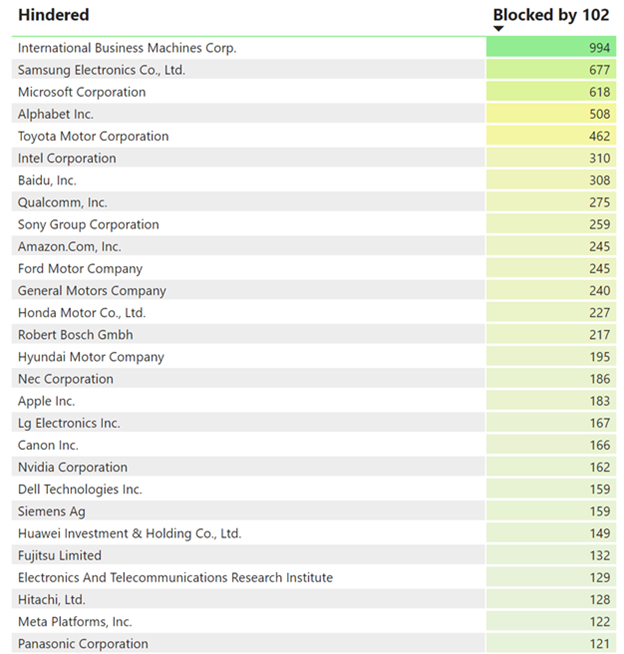
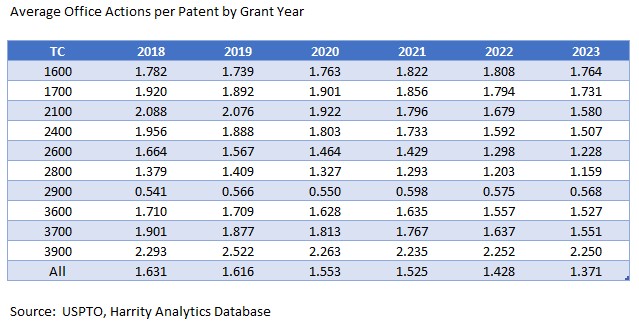
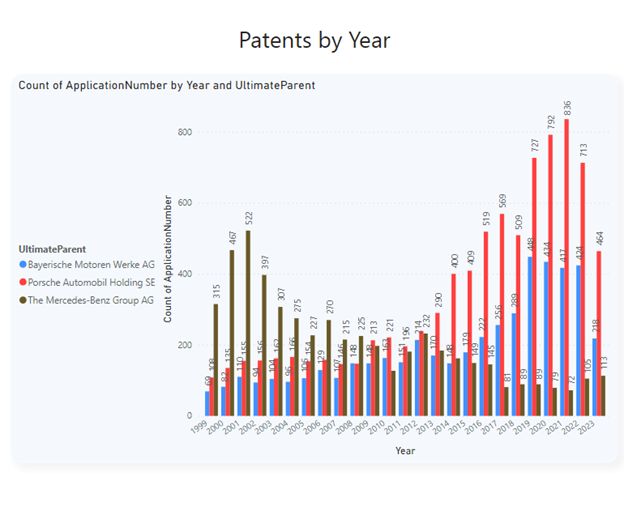
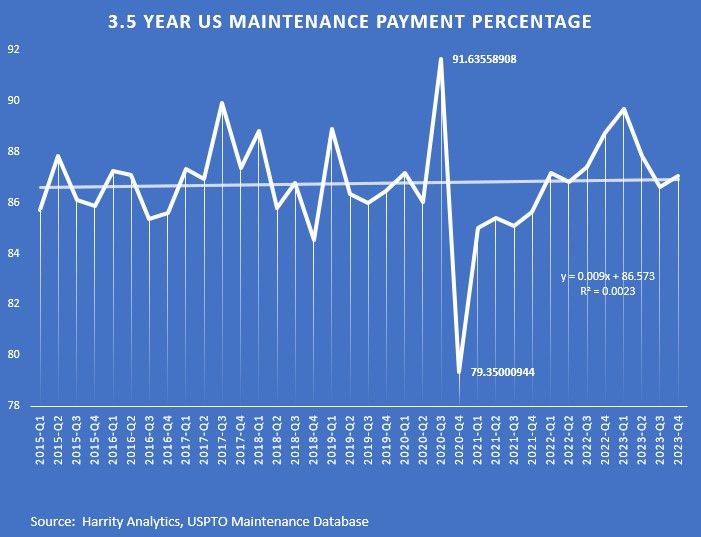
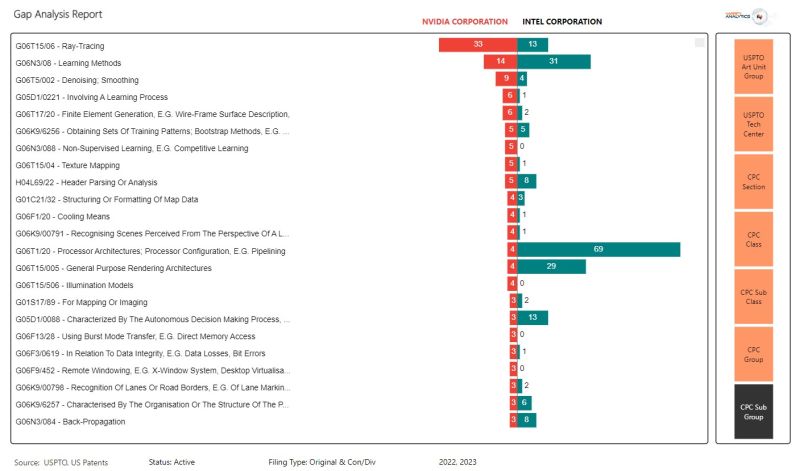
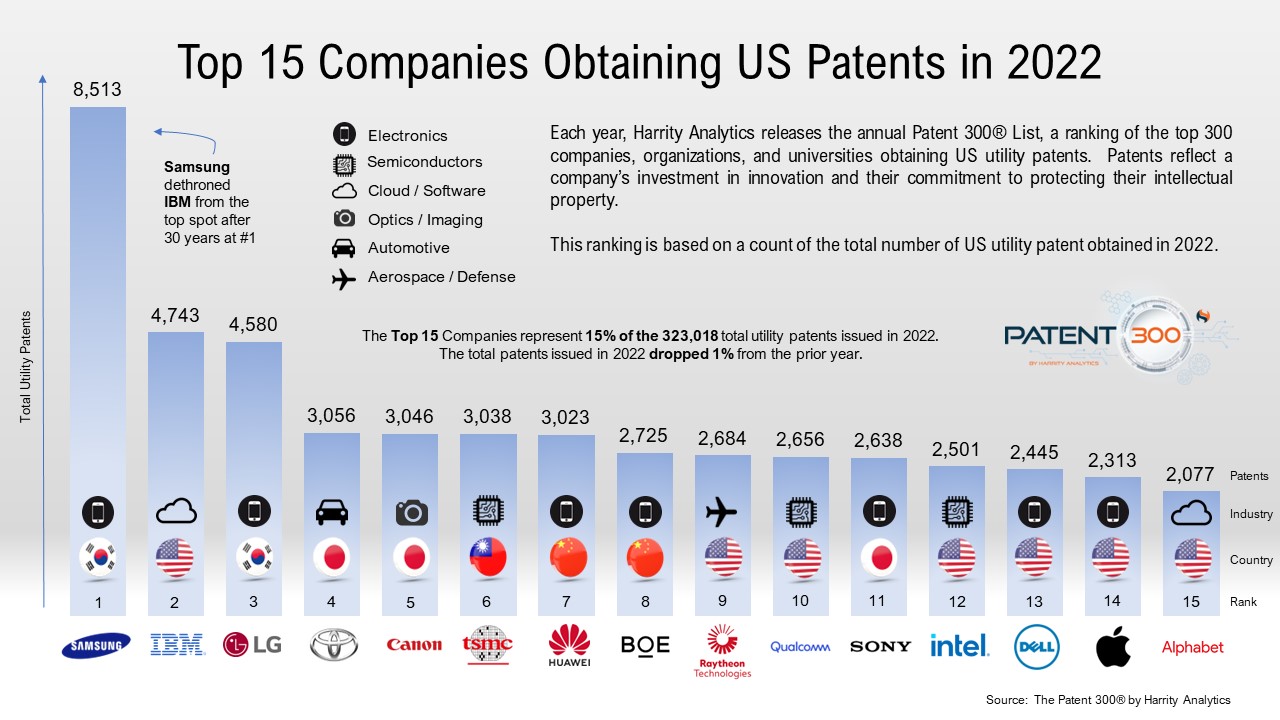
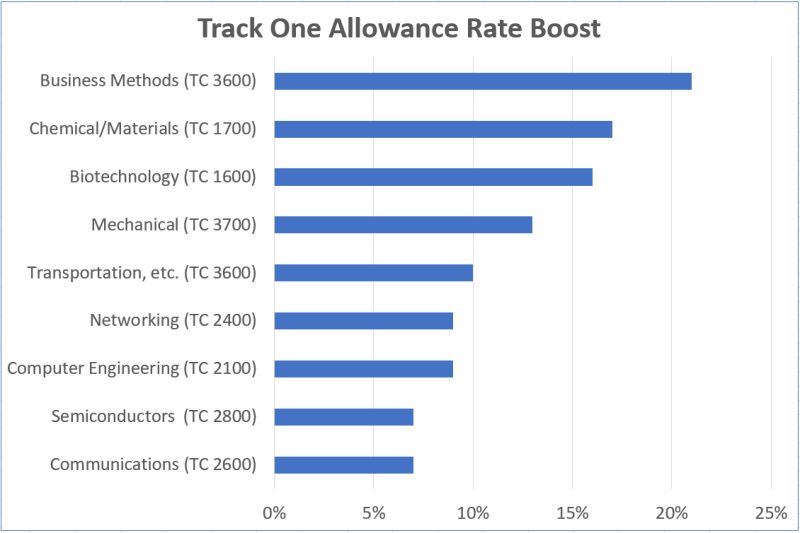
Law360 (October 16, 2019, 2:04 PM EDT) —
John Harrity has served as managing partner of
Harrity & Harrity LLP, the patent law firm he founded in 1999 with twin brother Paul Harrity, since 2016. During that time, the law firm’s revenue has grown by 127%, profits have gone up by 167% and the attorney headcount increased by 100%.
Here, Harrity discusses how his law firm has streamlined and automated the patent application process a la McDonald’s, why lawyers are not paid based on origination credits and why charity is such a big part of the firm’s culture.
How is your law firm different from a traditional law firm?
There’s a lot of ways that we’re different. From the very beginning, we’ve had this focus on quality. People talk about quality in our field, but one of the things we like to do when we talk about something is we want to make sure that it’s measurable. From the very beginning of our firm, my twin brother and I, we started with the traditional question: Why us? Why would anyone send us work over the thousands of firms doing patent prosecution and preparation? After some discussion, we honed in on quality. We implemented a couple of procedures, one was adopted from my brother’s former firm, Finnegan, and the other we created on our own.
We made sure everything goes through a very thorough second attorney review. It’s all about expectations here. Attorneys know that when they hand something in to me, there’s a certain level of quality that’s expected. And when we send things out to clients, there’s a certain expectation. When we send it to an inventor or in-house counsel, we’re going to send something that thoroughly, accurately and technically describes your invention and in our eyes is ready to be filed.
It’s tracking some statistics in relation to that to see: Are we succeeding or are we failing? How often, when we send out a patent application to an inventor or in-house counsel, do we get “looks good” [in response]? That’s our level of expectation. Going back to the beginning of the firm, so over the course of 20 years and having drafted over 5,000 patent applications, 67% of the time we’ve gotten a “looks good.”
The other [quality procedure] is writing style. I liken it to McDonald’s. Why is McDonald’s successful? Every McDonald’s you go to in the United States and you order their premier burger, the Big Mac, it’s going to have the same look, the exact same flavor every single time. And it’s going to come out in roughly the same amount of time. Our uniform writing style works exactly the same. Individual companies have preferences for how they want their patents to look, often the attorneys that work internally have individual preferences. We have a uniform writing style for every single attorney and every single company so that when they come to our firm, regardless of the drafting professional, they’re going to get their uniform writing style every single time.
Your firm has eliminated origination credits. Why have you done that and what kind of impact does it have?
Let’s think about origination credits. When you look inside these firms that have origination credits, what you see inside these firms are law firms within a law firm. You’ve got all of these partners with their origination credit, rowing in different directions. When you look at my firm, every client here is the firm’s client. We make business decisions about whether to bring on a client and whether to keep a client. Our firm’s mission is to be the No. 1 firm in the world doing what we do. We do patent applications and prosecution and we just do it in the electrical and mechanical space. I can tell you, every single individual at my firm, we’re all rowing in the same direction. Since we opened up 20 years ago, every single client has been the firm’s client. I might manage some of them and be the face to our firm for a particular client, but it’s the firm’s client, it’s not mine. That’s why we can be so agile, and move so quickly in the field, because we’re all rowing in the same direction.
How does the law firm then figure out how to determine whether a particular lawyer is successful?
We track some statistics internally. Every patent application that’s drafted at my firm, every response to a rejection from the patent office that’s drafted, goes through a second attorney review. And if I’m the reviewer, I fill out a scorecard and I’m grading this application or response on a little over a dozen different categories. This gives feedback to our attorneys. You can see your statistics for the year, you can compare them to last year. If you’re struggling in a particular area of drafting a patent application, don’t you want to know what that area is? There’s a quality score that all of our attorneys have.
There’s also a production element. One of the things we do is we pay our attorneys for production. We’ve experienced, in the lifetime of this firm, the same thing other firms experienced. The pricing of patent applications continually went up from 1999 until it plateaued for four to five years and then we started seeing it dip and it’s come down almost all the way to 1999 numbers. Back in 2013, one of our clients decreased their prices and we had a discussion internally and said, this is a wake-up call. We can walk away from the client and say we only do work for top-paying clients. If we do that, there will be less and less companies willing to pay top dollar and every firm in the United States is going to be lined up fighting for that work. The other route, the one we chose, is: Let’s get efficient. I put [the patent application process] in steps. Which of these steps must be performed by an attorney? All of the other steps, I hand those off to support staff members. And then, at the beginning of this year, I said: Let’s start automating some of the stuff the support staff is doing and let’s start automating some of the stuff the attorneys are doing.
2012 was before our efficiency journey. Our top drafting attorney drafted 54 patent applications that year, second place was 42. Last year, we had four attorneys draft more than 90 patent applications. We had one attorney in December draft 19 patent applications. This year our automation tools have rolled out. We have an attorney this year who is on track to draft 150 patent applications.
Let me tie that back into pay. You join our firm and when you’re assigned a patent application to draft, you’re given a number of hourly credits. If the hourly credit is 40 hours, you get that same hourly credit regardless of your actual time spent on it. So if you spend 40 hours, you’re getting hour-for-hour credit. If I can get you efficient, without sacrificing quality, down to 20 hours, now you’re drafting two patent applications. If I can get you down to 10 hours, then in that same 40 hour period you’re drafting four, which means you make four times as much money. The big producers at our firm make what partners make at other firms.
What tasks and processes have you automated?
One simple one I‘ll tell you about is form filling. There are certain forms that need to be filled out when you’re filing a patent application. And these forms were taking our staff about 15 to 30 minutes. Now it takes them about five seconds to fill them out — it’s being populated based on our docketing system.
You had a massive heart attack in 2016 at age 49, how has that impacted the way you operate your law firm?
Let me start with charity. I had this health scare back in 2016 and it really set the firm on a different course. I was in intensive care for eight weeks. It took me a couple of months after that to actually get back to the firm. I became hugely service-focused and that bled over to everything we do at the firm now. Harrity for Charity, that’s our giving back initiative. We’ve committed at the partner level to give 5% of profits to our partner charities. Those are the American Heart Association, that was my health scare, I had a heart attack; Inova Children’s Hospital; UNICEF; and Zero, which is the fight against prostate cancer. What makes Harrity for Charity infinitely better than the 5% coming out of partner profits is every single employee at my firm is committing a portion of their paycheck to one or more of these partner charities. Service is hugely important to us.
On the diversity side, we started our diversity journey kind of late in the game. We started our firm in 1999 and we started diversity efforts in November, 2015. At the time we started the conversation, we were 8% [ethnically] diverse at the attorney level. We implemented our Rooney Rule 2.0. What we’ve done is this. For every single position at my firm, support staff included, when we interview a white male for a position, we will interview a non-white male for that same position. Fast forward three years and we’ve gone from 8% diverse to 30% diverse today.
The newest thing we did is our minority firm incubator. It is a unique, innovative program. We’re willing to spend the time and money to make this thing successful. What we’re doing is creating minority-owned firms, female-owned firms that are replicas of our firm. We’re going to teach them what we do here and spin them off into their own firms. What makes the program a truly once-in-a-lifetime opportunity is we’re going to line up companies that will commit to give work to these minority-owned firms. Accenture has already made that commitment. The biggest pain point any time you start your own business is: Where am I going to get the work? We’re going to get [top patent-owning] companies to make that commitment to try them out.
They’re completely independent. They’re with us for three years; the fourth year, they leave our firm to start their own.
Harrity & Harrity is a patent preparation and prosecution firm specializing in the electrical and mechanical technology areas and is considered a Go-To Firm for the Patent 300™. Our clients have come to trust in our high-quality work, experienced people, industry leading innovation, and outstanding service. For more information, visit harrityllp.com.